What is hashing? Explain hash collision and any one collision resolution technique.
What is Hashing?
- Sequential search requires, on the average O(n) comparisons to locate an element, so many comparisons are not desirable for a large database of elements.
- Binary search requires much fewer comparisons on the average O (log n) but there is an additional requirement that the data should be sorted. Even with best sorting algorithm, sorting of elements require O(n log n) comparisons.
- There is another widely used technique for storing of data called hashing. It does away with the requirement of keeping data sorted (as in binary search) and its best case timing complexity is of constant order O(1). In its worst case, hashing algorithm starts behaving like linear search.
- Best case timing behavior of searching using hashing = O(1)
- Worst case timing Behavior of searching using hashing = O(n)
Collision Resolution Strategies
- Collision resolution is the main problem in hashing.
- If the element to be inserted is mapped to the same location, where an element is already inserted then we have a collision and it must be resolved.
- There are several strategies for collision resolution. The most commonly used are :
- Separate chaining - used with open hashing
- Open addressing - used with closed hashing
Separate chaining
- In this strategy, a separate list of all elements mapped to the same value is maintained.
- Separate chaining is based on collision avoidance.
- If memory space is tight, separate chaining should be avoided.
- Additional memory space for links is wasted in storing address of linked elements.
- Hashing function should ensure even distribution of elements among buckets; otherwise the timing behaviour of most operations on hash table will deteriorate.
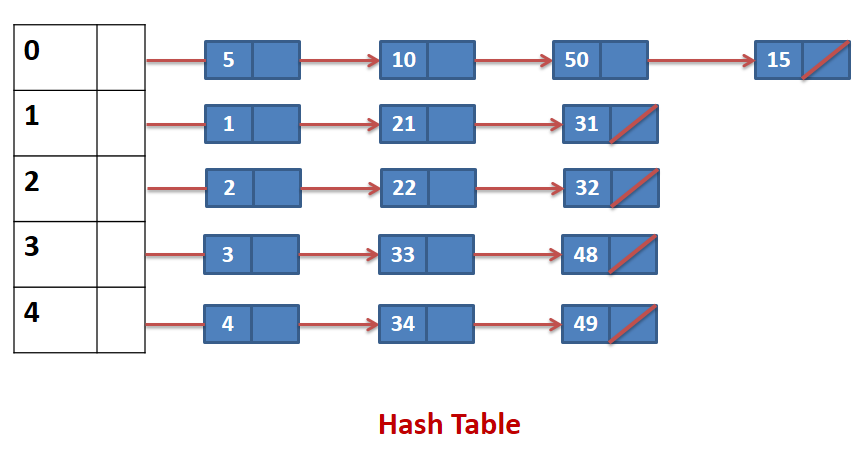
- Example : The integers given below are to be inserted in a hash table with 5 locations using chaining to resolve collisions. Construct hash table and use simplest hash function.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 21, 22, 33, 34, 15, 32, 31, 48, 49, 50
- An element can be mapped to a location in the hash table using the mapping function key % 10
| HASH TABLE LOCATION |
MAPPED ELEMENTS |
| 0 |
5, 10, 15, 50 |
| 1 |
1,21,31 |
| 2 |
2,22,32 |
| 3 |
3,33,48 |
| 4 |
4,34,49 |