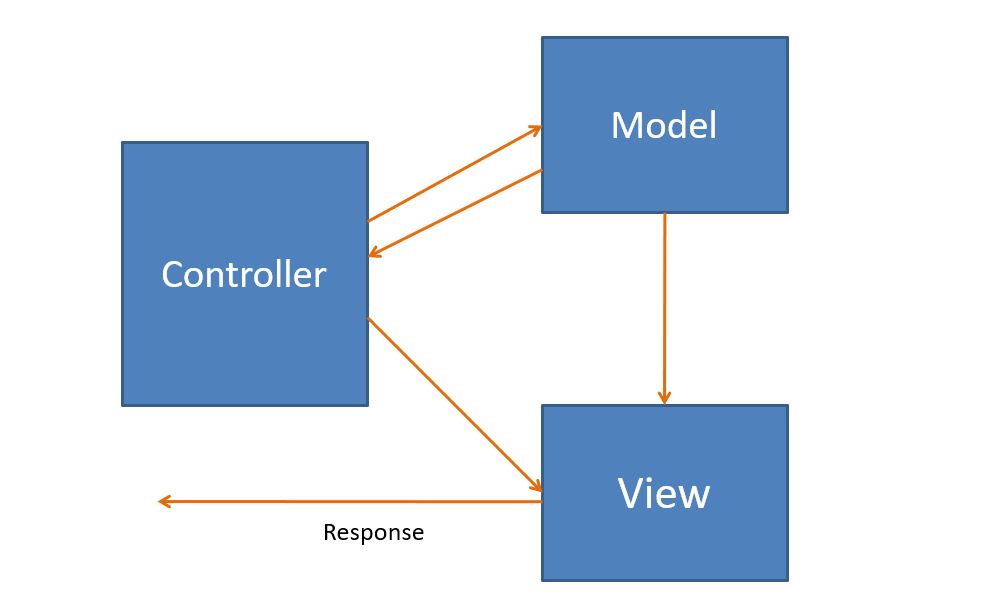
What is MVC Architecture?
- MVC stands for Model-View-Controller. This pattern is used to separate application's concerns.
-
Model - Model represents an object or JAVA POJO carrying data. It can also have logic to update controller if its data changes.
-
View - View represents the visualization of the data that model contains.
-
Controller - Controller acts on both model and view. It controls the data flow into model object and updates the view whenever data changes. It keeps view and model separate
(Figure: MVC)
Spring Architecture
(Figure: Spring Architecture)
-
Spring links objects together instead of the objects linking themselves together.
-
Spring object linking is defined in XML files, allowing easy changes for different application configurations thus working as a plug in architecture.
-
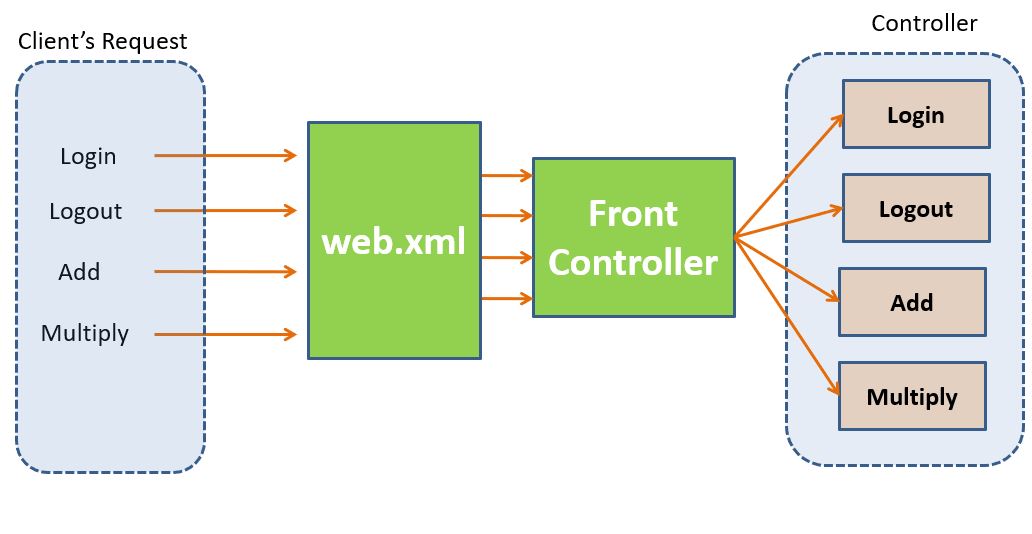
In an MVC architecture the controllers handle all requests.
-
Spring uses a “DispatcherServlet” defined in the web.xml file to analyze a request URL pattern and then pass control to the correct controller by using a URL mapping defined in a “Spring bean” XML file.