Hash function map several keys into same address called collision. How collision resolution techniques work?
- Collision resolution is the main problem in hashing.
- If the element to be inserted is mapped to the same location, where an element is already inserted then we have a collision and it must be resolved.
- There are several strategies for collision resolution. The most commonly used are :
- Separate chaining - used with open hashing
- Open addressing - used with closed hashing
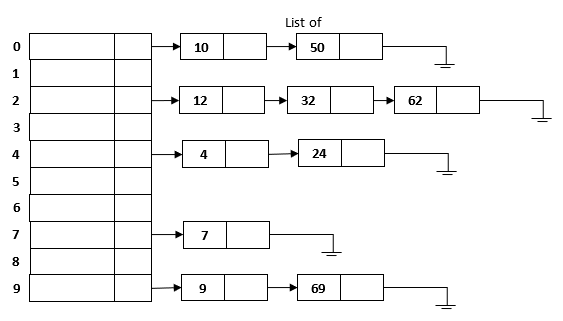
Separate chaining
- In this strategy, a separate list of all elements mapped to the same value is maintained.
- Separate chaining is based on collision avoidance.
- If memory space is tight, separate chaining should be avoided.
- Additional memory space for links is wasted in storing address of linked elements.
- Hashing function should ensure even distribution of elements among buckets; otherwise the timing behavior of most operations on hash table will deteriorate.
Open Addressing
- Separate chaining requires additional memory space for pointers. Open addressing hashing is an alternate method of handling collision.
- In open addressing, if a collision occurs, alternate cells are tried until an empty cell is found.
- Linear probing
- Quadratic probing
- Double hashing.
- In linear probing, whenever there is a collision, cells are searched sequentially (with wraparound) for an empty cell.
- Fig. shows the result of inserting keys {5,18,55,78,35,15} using the hash function (f(key)= key%10) and linear probing strategy.
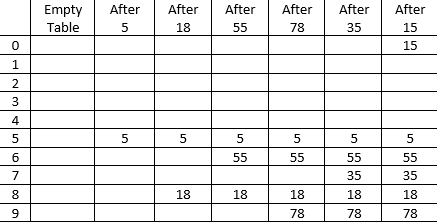
- Linear probing is easy to implement but it suffers from "primary clustering".
- When many keys are mapped to the same location (clustering), linear probing will not distribute these keys evenly in the hash table. These keys will be stored in neighborhood of the location where they are mapped. This will lead to clustering of keys around the point of collision.