The spiral model is suitable for normally suits for development of large-scale software system.
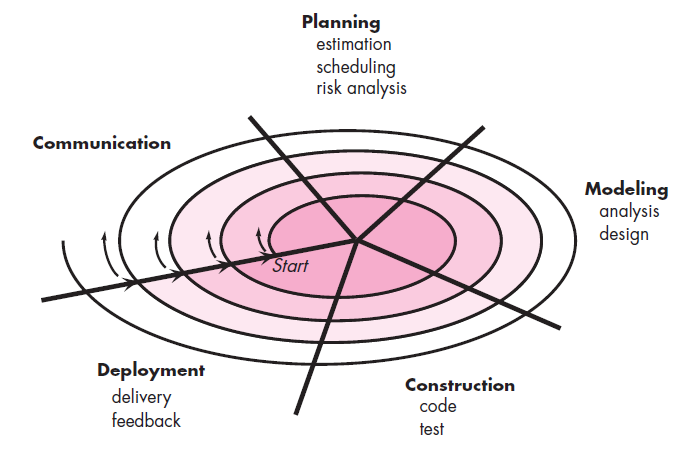
(Figure: Spiral Model)
- The Spiral model is an evolutionary process model that couples iterative nature of prototyping with the controlled and systematic aspects of waterfall model
- It provides the potential for rapid development.
- Software is developed in a series of evolutionary releases.
- Early iteration release might be prototype but later iterations provides more complete version of software.
- It is divided into framework activities. Each activity represent one segment of the spiral
- Each pass through the planning region results in adjustments to
- the project plan
- Cost & schedule based on feedback
When to use Spiral Model?
- For development of large scale / high-risk projects.
- When costs and risk evaluation is important.
- Users are unsure of their needs.
- Requirements are complex.
- New product line.
- Significant (considerable) changes are expected.
Advantages
- High amount of risk analysis hence, avoidance of Risk is enhanced.
- Strong approval and documentation control.
- Additional functionality can be added at a later date.
- Software is produced early in the Software Life Cycle.
Disadvantages
- Can be a costly model to use.
- Risk analysis requires highly specific expertise.
- Project’s success is highly dependent on the risk analysis phase.
- Doesn’t work well for smaller projects.