List the different Agile Process Model and Explain any one with suitable example.
List the different Agile Process Model
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- Scrum
- Feature Driven Development (FDD)
- Crystal
- Agile Modelling (AM)
Extreme Programming
- The most widely used approach to agile software development
- A variant of XP called Industrial XP (IXP) has been proposed to target process for large organizations
- It uses object oriented approach as its preferred development model
- Communication: To achieve effective communication, it emphasized close & informal (verbal) collaboration between customers and developers
- Simplicity: It restricts developers to design for immediate needs not for future needs
- Feedback: It is derived from three sources the implemented software, the customer and other software team members, it uses Unit testing as primary testing
- Courage: It demands courage (discipline), there is often significant pressure to design for future requirements, XP team must have the discipline (courage) to design for today
- Respect: XP team respect among members
- It considers four framework activities
- Planning
- Design
- Coding
- Testing
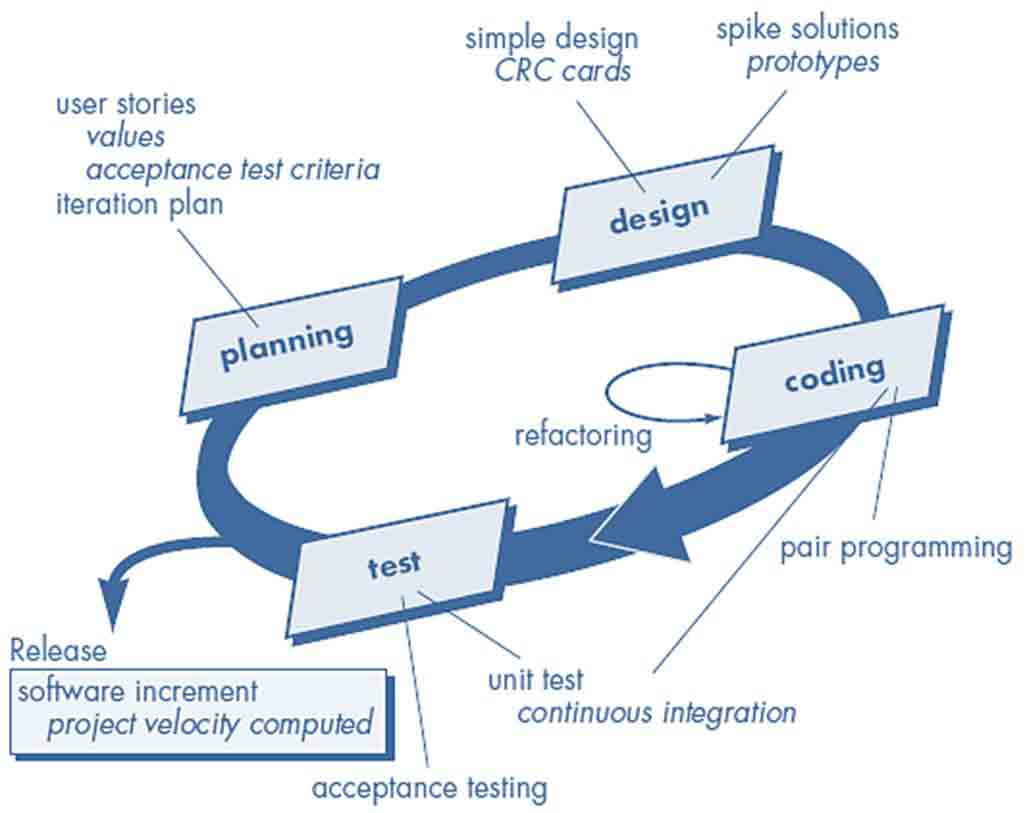
(Figure: XP Process)
Planning
- User Stories
- Customers assigns value (priority)
- Developers assigns cost (number of development weeks)
- Project velocity
- Computed at the end of first release
- Number of stories implemented in first release
- Estimates for future release
- Guard against over-commitment
Design
- Keep-it-Simple (Design of extra functionality is discouraged)
- Preparation of CRC card is work project, CRC cards identify and organize object oriented classes
- Spike Solutions, Operational prototype intended to clear confusion
- Refactoring
- Modify internals of code, No observable change
Coding
- Develops a series of Unit test for stories included in current release
- Complete code perform unit-test to get immediate feedback
- XP recommend pair-programming, “Two heads are better than one”
- Integrate code with other team members, this “continuous integration” helps to avoid compatibility & interfacing problems, “smoke testing” environment to uncover errors early
Testing
- Unit test by developers & fix small problems
- Acceptance tests - Specified by customer