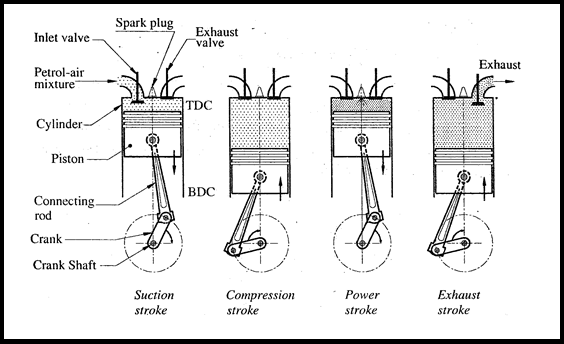
Discuss the construction and working of four stroke Petrol engines.
The whole cycle is completed in four strokes,
- Suction stroke
- Compression stroke
- Working or Power stroke
- Exhaust stroke
Suction Stroke
- During this stroke, inlet valve remains open and exhaust valve is closed, the pressure in the cylinder will be atmospheric.
- The piston moves from TDC to BDC. So the volume in the cylinder increases, while simultaneously the pressure decreases.
- This creates a pressure difference between the atmosphere and inside of the cylinder. Due to this pressure difference the petrol and air mixture will enter into the cylinder through carburetor.
- At the end of this stroke piston reaches at BDC, the cylinder will be filled completely with petrol and air mixture called charge and inlet valve is closed.
Compression Stroke
- During this stroke both the inlet valve and exhaust valve remains closed. Piston moves from BDC to TDC.
- As this stroke is being performed, the petrol and air mixture contained in the cylinder will be compressed, so pressure and temperature of mixture increases.
- Near the end of this stroke, the petrol and air mixture is ignited by electric spark given out by the spark plug.
- The combustion of the petrol releases the hot gases which will increase the pressure at constant volume.
Power or Expansion Stroke
- During this stroke both the inlet valve and exhaust valve remain closed, the piston moves from TDC to BDC.
- The high pressure and high temperature burnt gases force the piston to perform this stroke, called power stroke.
- This stroke is also known as expansion or working stroke.
- The engine produces mechanical work or power during this stroke.
- As the piston moves from TDC to BDC, the pressure of hot gases gradually decreases and volume increases.
- This will suddenly bring the cylinder pressure to the atmospheric pressure.
Exhaust Stroke
- During this stroke, the exhaust valve opens and the inlet valve remains closed.
- The piston moves from BDC to TDC and during this motion piston pushes the exhaust gases out of the cylinder at constant pressure.
- At the end of the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve is closed and inlet valve will open. Then there will be again a suction stroke and the same cycle will be repeated.