Discuss UV-VIS method for band gap measurement of semiconductor.
- UV- Vis Spectroscopy is related to the interaction of light with matter.
- As light is absorbed by matter, the result is an increase in the energy content of the atoms or molecules.
- This method is used to measure the energy band gap of different materials, by measuring absorption spectrum.
- Bandgap refers to the energy difference between bottom of conduction band and top of valence band, through which electrons are able to jump from one band to another.
- The instrument used in UV-Vis spectroscopy is called UV-Vis spectro-photometer.
- It measure the intensity of light after passing through a sample (I), and compares it to the intensity of light before it passes through the sample (I0).
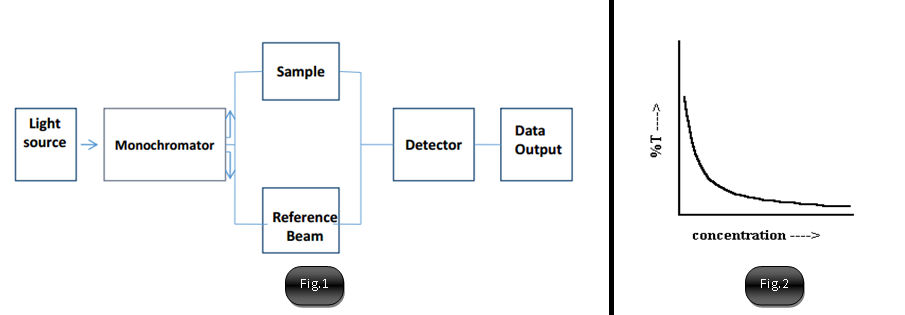
- A light of wavelength (λ) and energy (hv) is made to pass through monochromator to get a parallel beam.
- It then passes through a beam splitter and is incident on two cells, a reference cell and a sample cell.
- The intensities of light from reference and sample cells is collected by the detector.
- The ration of intensities is called transmittance (T).
i.e.
- The transmittance (T) is usually expressed in percentage (%T).
- If we plot %T w.r.t. to concentration of sample, we get an exponential decrease in transmittance, with an increase in concentration.
- Higher the concentration, more is the absorption so less is the value of I, through the sample cell.
- As it is difficult to extract characteristics from the exponential relation, we define a relation absorption (A)
Absorption
- The Tauc’s relation is used to determine the bandgap in semiconductor.
,
Rearranging above relation, we can have
Where, absorption coefficient
Where, transmittance
Where, Thickness of the sample
Where, for direct allowed, indirect allowed, direct forbidden and indirect forbidden transitions respectively.
Where,
Now, we can plot a graph of along x - axis vs hv (along y - axis), we will get slop as and y intercept as Eg. Dividing y intercept by we can estimate the band gap.